LEISHMANIOSE
It is an infect contagious disease, that it can be classified
as zoonose, for the fact of being transmissible of the animals to the man, and
vice and it turns, caused by a protozoan (Leishmania), that has the egg-round
form and it attacks some cells BLOOD called macrófagos. They are several the
species of that group capable to cause the disease, but all have the fact in
common of they need, to reproduce and to reach the adult form, of a spineless
host, obligatorily a mosquito, call, in Brazil, of Biriguís, Mosquito Palha,
Mosquito gunpowder or Cangalhinha. Such have night habits, attacking your
victims in general for sugar blood in the evening and beginning of the night,
and of that bite they transmit for the new host (animal or the man), the
disease, that assumes two different forms: CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIOSE OR TEGUMENTAR
and VISCERAL LEISHMANIOSE.
Visceral Leishmaniose, is frequently that found among the
sensitive animals as the dog or the cat, besides the guinea-pig used at
laboratory.
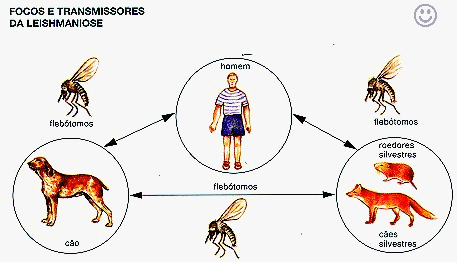
The mosquito host, to the sugar blood of an animal (or of the
man) infected, it is contaminated, and in your intestines and glands you
salivate the protozoan he/she multiplies. When those mosquitos porteriormente
sugarem blood of another animal inject the forms infectantes of Leishmania, the
one which falling of the sanguine circulation of the new host (called definitive
host), it reproduces the disease.
 The incubation period (period that is going of the bite for
the mosquito infected until the emergence of the first symptoms) it varies
between 10 and 25 days, being able to, in the however, to arrive until one year.
After that period they appear pápulas in general in the skin of the animal or
of the infected man, pápulas those anything characteristics, however
proriginosas (they scratch) determining sensation of heat and pain. It also
happens in that phase the inflammation of the close ganglions the bite for the
mosquito. In this phase, starting from the analysis of the collected material of
the inflamed ganglions it can be found the forms infectantes of the protozoan.
The ganglion inflamed lymphatic necrosa, and harmed like this it ends for coming
to I hole to evacuate that festering material, being at your place an ulcer,
denominated of cancer espúndico. In that phase the disease is easily
diagnosticavel for the exhibition of characteristic cutaneous ulcers.
The incubation period (period that is going of the bite for
the mosquito infected until the emergence of the first symptoms) it varies
between 10 and 25 days, being able to, in the however, to arrive until one year.
After that period they appear pápulas in general in the skin of the animal or
of the infected man, pápulas those anything characteristics, however
proriginosas (they scratch) determining sensation of heat and pain. It also
happens in that phase the inflammation of the close ganglions the bite for the
mosquito. In this phase, starting from the analysis of the collected material of
the inflamed ganglions it can be found the forms infectantes of the protozoan.
The ganglion inflamed lymphatic necrosa, and harmed like this it ends for coming
to I hole to evacuate that festering material, being at your place an ulcer,
denominated of cancer espúndico. In that phase the disease is easily
diagnosticavel for the exhibition of characteristic cutaneous ulcers.
In some cases, in the however, the cutaneous disease assumes
forms non ulcerous, impetiginoide calls or tuberiformes. The evolution of the
disease without appropriate treatment, takes to serious lesions and deformantes,
besides with losses a lot of unrecoverable times of the nose and of the
epidermis of the face.
In your visceral form, the lesions being internal, mainly in
the spleen, they are translated by increase of volume of that organ
(esplenomegalia), besides fever and abdominal pain. Your evolution also takes to
an increase of volume of the liver.
PROPHYLAXIS OF THE DISEASE
The most efficient prevention measure is the combat to the
mosquito host, impeding him/it of multiplying. That measured it is possible with
the application of insecticides in your criatórios. Parallel, isolation
of the sick definitive hosts, or your treatment when possible.
DIAGNOSIS
A test exists, created by a Brazilian cientist in 1926 that
it is quite efficient and it consists of a simple allergic reaction, obtained by
the inoculation by road intra-dérmica of a leptomonas suspension to which the
phenol was joined for your sterilization. They exist however some clinical signs
that can help:
-
accentuated weigh loss and reduction
-
atrophies muscular
-
cyclical
hipertermia
-
anemia
-
fall of
the hair, especially in the head and it breaks inferior of the thorax
and tail, accompanied of an rash of the skin
-
excessive growth of the fingernails.
TREATMENT
Several medicines quimioterápicos were already used, however
all determining serious secondary reactions parallel, what makes unfeasible your
treatment, to not to be in very few cases, and in these forcing direct and
permanent medical accompaniment.
PREVENTIVE
VACCINATION
In animals it is not used and given the difficulty of
efficient treatment of the infected animals, as well as serious secondary
reactions when the treatment is tried, the sacrifice of the sick animals is
prescribed, mainly in if treating of the dog or of the cat, with the objective
of like this to impede the human infection.
People infected with the parasite, they should be
obligatorily isolated in appropriate place, in order to be to interrupt the
chain evolutina of the protozoan. It is treated, in the however, of a disease
called ezótica, happily present in very few places of the Brazilian territory.
For those characteristics, when diagnosed a fóco of the disease, they are made
necessary energetic measures for your eradication, under penalty of your
disseminação.
Carmello Liberato Thadei (Veterinary Doctor -CRMV-SP-0442)
 The incubation period (period that is going of the bite for
the mosquito infected until the emergence of the first symptoms) it varies
between 10 and 25 days, being able to, in the however, to arrive until one year.
After that period they appear pápulas in general in the skin of the animal or
of the infected man, pápulas those anything characteristics, however
proriginosas (they scratch) determining sensation of heat and pain. It also
happens in that phase the inflammation of the close ganglions the bite for the
mosquito. In this phase, starting from the analysis of the collected material of
the inflamed ganglions it can be found the forms infectantes of the protozoan.
The ganglion inflamed lymphatic necrosa, and harmed like this it ends for coming
to I hole to evacuate that festering material, being at your place an ulcer,
denominated of cancer espúndico. In that phase the disease is easily
diagnosticavel for the exhibition of characteristic cutaneous ulcers.
The incubation period (period that is going of the bite for
the mosquito infected until the emergence of the first symptoms) it varies
between 10 and 25 days, being able to, in the however, to arrive until one year.
After that period they appear pápulas in general in the skin of the animal or
of the infected man, pápulas those anything characteristics, however
proriginosas (they scratch) determining sensation of heat and pain. It also
happens in that phase the inflammation of the close ganglions the bite for the
mosquito. In this phase, starting from the analysis of the collected material of
the inflamed ganglions it can be found the forms infectantes of the protozoan.
The ganglion inflamed lymphatic necrosa, and harmed like this it ends for coming
to I hole to evacuate that festering material, being at your place an ulcer,
denominated of cancer espúndico. In that phase the disease is easily
diagnosticavel for the exhibition of characteristic cutaneous ulcers.